プレMAF療法 プレMAFの技術情報 マクロファージとは Pre-MAF therapy Pre-MAF technical information What are macrophages?
Pre-MAF technical information
Toppage
- Pre-MAF technical information
Experiments on pre-MAF
- Study to evaluate phagocytic activity using murine peritoneal macrophages (results of collaborative research with Tokushima University)
-
Study method
The cervical spines of ICR mice (, 8 weeks) were dislocated to harvest mouse peritoneal macrophages. After harvesting, the cells were adjusted to 1.0 x 106 cells/mL using a Burker-Turk hemocytometer. Sterilized coverslips were placed in a 24-well plate, and the collected and adjusted peritoneal cell fluid was dispensed at 5.0 x 105 cells/well, after which the macrophages were allowed to attach to the coverslips (37°C, 1 hour). After attaching, the peritoneal cell fluid was collected in an Eppendorf tube, and samples (Gc globulin, pre-MAF) and RPMI medium (control) for comparisons were added and reacted (37°C, 1 hour). The coverslips on which the macrophages had settled were washed with RPMI medium and incubated (37°C, 15 hours). After incubation, the peritoneal fluid-treated samples were added to each well to stimulate the macrophages (37°C, 3 hours), and 0.5% opsonized SRBC was added to induce phagocytosis (37°C, 1.5 hours). After phagocytosis, the cells were washed, stained with Giemsa, and examined under a microscope.
*: RPMI medium only
Study results

This shows that the administration of pre-MAF activates macrophages, a type of immune cell, but that Gc globulin does not, suggesting that the conversion from Gc globulin to pre-MAF is necessary.
- Study to evaluate changes in phagocytic activity over time using murine peritoneal macrophages (results of collaborative research with Tokushima University)
-
Study method
The cervical spines of ICR mice (, 8 weeks) were dislocated to harvest mouse peritoneal macrophages. After harvesting, the cells were adjusted to 1.0 x 106 cells/mL using a Burker-Turk hemocytometer. Sterilized coverslips were placed in a 24-well plate, and the collected and adjusted peritoneal cell fluid was dispensed at 5.0 x 105 cells/well, after which the macrophages were allowed to attach to the coverslips (37°C, 1 hour). After attaching, the peritoneal cell fluid was collected in an Eppendorf tube, and samples (Gc globulin, pre-MAF) and RPMI medium (control) for comparisons were added and reacted (37°C, 1 hour). The coverslips on which the macrophages had settled were washed with RPMI medium and incubated (37°C, 15 hours). After incubation, the peritoneal fluid-treated samples were added to each well to stimulate the macrophages (37°C, 3 hours), and 0.5% opsonized SRBC was added to induce phagocytosis (37°C, 1.5 hours). After phagocytosis, the cells were washed, stained with Giemsa, and examined under a microscope.
*: RPMI medium only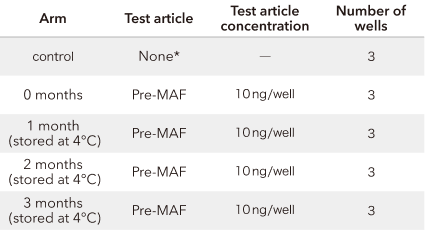
Study results
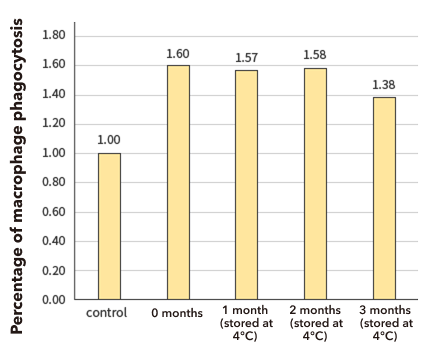
This suggests that pre-MAF activates macrophages even after 3 months in refrigerated storage.
- Assessment of phagocytic capability of human PBMC adherent cell fractions (results of collaborative research with the Jikei University School of Medicine)
-
Study method
Approximately 20 ml of peripheral blood was collected from healthy adult volunteers through heparin blood sampling. PBMCs were collected using the Ficoll density gradient centrifugation method, and cells were suspended in serum-free RPMI 1640 medium and inoculated onto a 10 cm Petri Dish. Pre-MAF (from Gc derived from the PBMCs of the same healthy volunteers) or PBS control was added to the PBMC culture media, and this was cultured for 4 hours. Thereafter, cells were washed with warm PBS, and suspended cells and the medium were removed. The phagocytic capability of cultured adherent cell fractions was measured using Phagocytosis Assay Kits (IgG FITC, Cayman), where fluorescent beads coated with IgG were added to the adherent cells and these were cultured for 90 minutes. Ten random fields were photographed by fluorescence microscopy after washing. Fluorescence micrographs were analyzed using WinROOF, and the absolute area of fluorescence in the photographs was determined and evaluated as the phagocytic capability of macrophages.
Study results
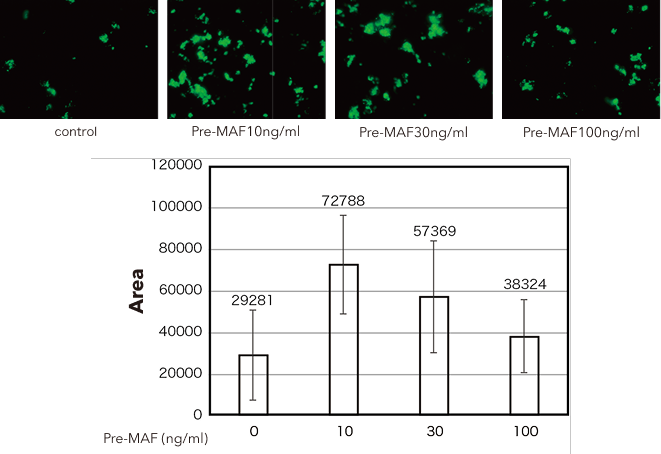
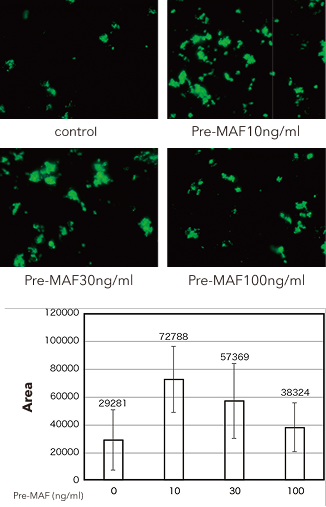
Human PBMC adherent cell fractions showed an obvious increase in phagocytic capability upon pre-MAF treatment, with the strongest increase in phagocytic capability observed with 10 ng/ml of pre-MAF.
- Study to evaluate antiangiogenic activity (results of activity outsourced to GeneStem Co., Ltd.)
-
Study method
48-well plates were coated with 200 μL/well of Matrigel, and HUVEC were cultured at 10000 cells/200 μL/well. Medium consisting of 1% FCS added to HuMedia-EB2 was used for the culture. Recombinant human VEGF165 (hVEGF165) was added to the medium to obtain a final concentration of 10 ng/ml, and test articles were added (refer to the Table below). Photographs were taken 12 to 16 hours after the initiation of the culture to quantify the length of tubes formed and branch points. Measurement results were compared between all arms using OMS's "Statcel2" statistical analysis software and tested for significant differences using one-way analyses of variance (ANOVA) and the Tukey-Kramer method.
*: 0.1% DMSO containing phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) (-) added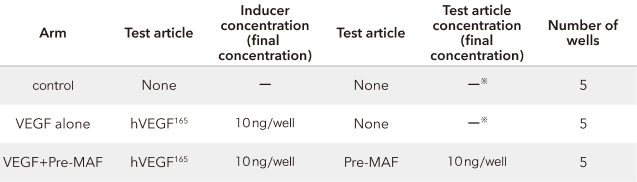
Study results

Pre-MAF administration has been shown to inhibit angiogenesis. In other words, this indicates that pre-MAF inhibits the proliferation of blood vessels that provide oxygen/nutrients to cancer cells. What is angiogenesis?
Cancer cells work to form new blood vessels to obtain the oxygen and nutrients they need to grow. This process of forming new blood vessels is called "angiogenesis." These new blood vessels may not only provide oxygen and nutrients to cancer cells but may also play a role in the pathway of cancer metastasis.
What is VEGF?
This is the abbreviation for vascular endothelial growth factor. The overexpression of VEGF, a group of glycoproteins involved in angiogenesis, has been reported to be associated with tumor angiogenesis and metastasis.
The thinking is that the proliferation of cancer cells is inhibited based on the following two points: that one's natural immune function is improved through the activation of macrophages and that the supply of oxygen and nutrients is inhibited through the inhibition of angiogenesis.
- Study to evaluate antitumor activity against murine lung cancer (results of collaborative research with Tokyo University of Science)
-
Study method
Lewis Lung Carcinoma (LLC) cells were cultured in 100 mm plastic dishes at 37°C and 5% CO2 in Dulbecco's Modified Eagle Medium containing 10% fetal bovine serum. After the removal of culture supernatant, LLC cells were suspended in phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) at 4°C and centrifuged at 4°C for 5 minutes at 200 x g, after which the supernatant was removed. Precipitated LLC cells were suspended in PBS at 4°C, and 2 x 105 LLC cells were injected via the tail vein of 6-week-old C57BL/6 mice (males) consisting of four animals per arm.
From Day 7 after the injection, 400 ng/kg of pre-MAF was administered for 10 consecutive days through intraperitoneal (i.p.), subcutaneous (s.c.), or intramuscular (i.m.) injections. The mice were sacrificed on the day after the last administration, and the number of tumor nodules formed in the lungs was counted under a stereoscopic microscope.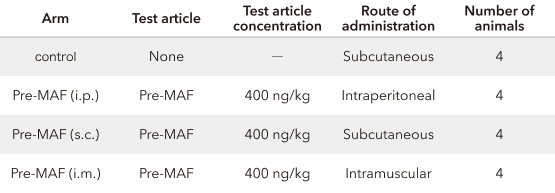
Study results
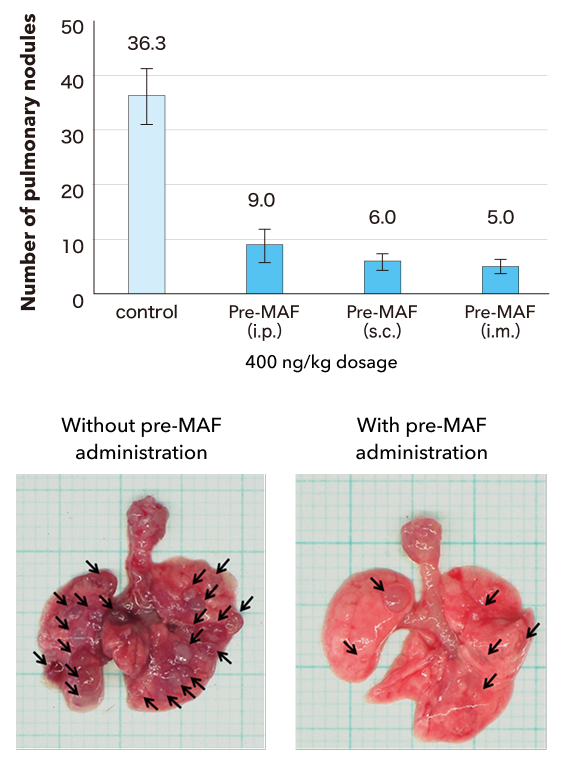
Pre-MAF was associated with a significant reduction in the number of lung tumors, irrespective of the route of administration. In other words, pre-MAF was shown to have an antitumor effect.
- Study to evaluate the effects in combination with antibody agents (results of collaborative research with the Jikei University School of Medicine)
-
Study method
A total of 106 OE19 cells/mouse were implanted subcutaneously in the back of nude mice. Mice were divided into four arms: a no-treatment arm, arms treated with pre-MAF, trastuzumab alone, or a combination. Pre-MAF was injected subcutaneously at a concentration of 10 ng/mouse for 10 consecutive days from Day 5 after implantation. Trastuzumab was administered intraperitoneally at a dose of 25 μg/mouse every three days starting on Day 5 after implantation, for a total of four administrations. Tumor cells were counted using calipers from two directions perpendicular to the tumor diameter at a frequency of once a week after implantation, and tumor sizes (mm2) were expressed as these measured values squared.
Study results

This clearly shows that tumor sizes were significantly smaller in the arm to which the combination with pre-MAF was administered compared to the arm to which the antibody (trastuzumab) alone was administered. In other words, an antitumor effect is seen with pre-MAF when used in combination with an antibody agent.
What is trastuzumab?
This is a type of molecular-targeted therapeutic agent that exerts its antitumor effect by specifically binding to HER2 proteins. After specifically binding to HER2, antitumor effects are exerted through antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC) with NK cells and monocytes as the acting cells.
- Toxicology study (results of activities outsourced to DIMS Institute of Medical Science, Inc.)
-
Study method
Six-week-old Crl:CD (SD) rats were divided into three arms, each with six males and females, based on weight stratification. After arm allocation, pre-MAF was administered subcutaneously once a week for 13 weeks to evaluate the toxic effects of intermittent subcutaneous administration.
*: Administration of Otsuka normal saline
No deaths or abnormalities were reported in either male or female animals given pre-MAF (4,000 ng/kg/day) for 13 consecutive weeks. This indicates that the no observed adverse effect level (NOAEL) for pre-MAF is no less than 4,000 ng/kg/day (240 µg/60kg/day).

