プレMAF療法 プレMAFの技術情報 マクロファージとは Pre-MAF therapy Pre-MAF technical information What are macrophages?
Pre-MAF technical information
Toppage
- Pre-MAF technical information
Detailed information about pre-MAF therapy
What is pre-MAF?
Pre-MAF*1is a glycoprotein produced by treating one's own glycoprotein type, "Gc globulin," with an enzyme (galactosidase). Pre-MAF responds to diseases by enhancing the body's natural immune function through the activation of macrophages, is tailored for each patient, and is individually order-made.
*1:“Abbreviation of "precursor" + "Macrophage Activating Factor"
What are macrophages?
Macrophages, a type of white blood cell, are also referred to as phagocytes or histiocytes. They are important cells responsible for the body's defense against pathogens and play a central role in innate immunity. They phagocytize and digest foreign substances, such as pathogens that have entered the body. Additionally, macrophages secrete various cytokines and lysosomal enzymes to activate T lymphocytes when they take up antigens. If tissue damage occurs, these cells release secretions according to the situation, contributing to hemostasis and thrombus formation.
Click here for details
What are Gc globulins?
These are also referred to as vitamin D-binding proteins.
・Localized on human chromosome 4q11-q13
・Has 13 introns and a 42 kb genetic makeup
・Human mature Gc globulin is 458 amino acids in length
・A major protein belonging to the albumin superfamily, accounting for 6% of α-globulin fractions
・Mainly produced in the liver
・Half-life of 1.7 to 2.5 days in human plasma
・The estimated daily production is approximately 700 to 900 mg/day (10 mg/kg/day) in adults
・30 to 50 mg/dL in sera
・50 to 55 kDa proteins
・Isoelectric point (IEP) of 4.9 to 5.1
・Less than 5% of Gc globulins, typically less than 2% are holoproteins, and almost all Gc globulins circulate as apoproteins
・Transports and stores all vitamin D metabolites, enhances neutrophil migration through complement components C5a and C5a des Arg, and functions as a cochemotaxin
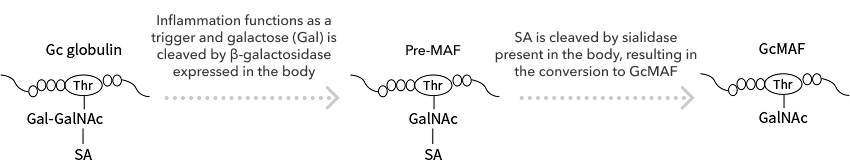
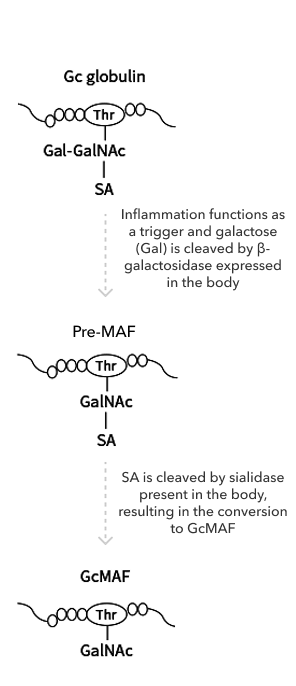
In general, the body is triggered by inflammation. Galactose (Gal) is cleaved by β-galactosidase expressed in the body, and SA is cleaved by sialidase present in the body, resulting in the conversion to GcMAF.
Functions of GcMAF
・Activating macrophages1)
・Activating osteoclasts2)
・Adjuvant effect in photodynamic therapy (PDT)3)
・Antiangiogenic activity4,7)
・Inducing apoptosis5)
・Morphologically changing tumor cells to normal cells6)
・Improving human neurometabolic activity via cAMP signaling7)
・Antitoxic effect on cadmium8)
・Increasing superoxide production1)
・Proliferation of peripheral blood mononuclear cells7)
・Antitumor activity9)
・Inhibiting the metastatic potential of human cancer cells in culture10)
1)Source: Mohamad SB, Nagasawa H, Uto Y, Hori H. Preparation of Gc protein-derived macrophage activating factor (GcMAF) and its structural characterization and biological activities. Anticancer Res. 2002 Nov-Dec;22(6C):4297-300.
2)Source:Swamy N, Ghosh S, Schneider GB, Ray R. Baculovirus-expressed vitamin D-binding protein-macrophage activating factor (DBP-maf) activates osteoclasts and binding of 25-hydroxyvitamin D(3) does not influence this activity. J Cell Biochem. 2001;81(3):535-46.
3)Source:Korbelik M, Naraparaju VR, Yamamoto N. Macrophage-directed immunotherapy as adjuvant to photodynamic therapy of cancer. Br J Cancer. 1997;75(2):202-7.
4)Source:Kisker O, Onizuka S, Becker CM, Fannon M, Flynn E, D'Amato R, Zetter B, Folkman J, Ray R, Swamy N, Pirie-Shepherd S. Vitamin D binding protein-macrophage activating factor (DBP-maf) inhibits angiogenesis and tumor growth in mice. Neoplasia. 2003 Jan-Feb;5(1):32-40.
5)Source:Thyer L, Ward E, Smith R, Fiore MG, Magherini S, Branca JJ, Morucci G, Gulisano M, Ruggiero M, Pacini S. A novel role for a major component of the vitamin D axis: vitamin D binding protein-derived macrophage activating factor induces human breast cancer cell apoptosis through stimulation of macrophages. Nutrients. 2013 Jul 8;5(7):2577-89.
6)Source:Pacini S, Punzi T, Morucci G, Gulisano M, Ruggiero M. Effects of vitamin D-binding protein-derived macrophage-activating factor on human breast cancer cells. Anticancer Res. 2012 Jan;32(1):45-52.
7)Source:Pacini S, Morucci G, Punzi T, Gulisano M, Ruggiero M. Gc protein-derived macrophage-activating factor (GcMAF) stimulates cAMP formation in human mononuclear cells and inhibits angiogenesis in chick embryo chorionallantoic membrane assay. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2011 Apr;60(4):479-85.
8)Source:Massimo G, Punzi T, Morucci G, Ruggiero M. Effects of Cadmium and vitamin D binding protein-derived macrophage activating factor (DBP-MAF) in human breast cancer cells. Italian Journal of Anatomy and Embryology, vol.116, n.1 Supplement, 91, 2011.
9)Source:Nonaka K, Onizuka S, Ishibashi H, Uto Y, Hori H, Nakayama T, Matsuura N, Kanematsu T, Fujioka H. Vitamin D binding protein-macrophage activating factor inhibits HCC in SCID mice. J Surg Res. 2012 Jan;172(1):116-22.
10)Source:Gregory KJ, Zhao B, Bielenberg DR, Dridi S, Wu J, Jiang W, Huang B, Pirie-Shepherd S, Fannon M. Vitamin D binding protein-macrophage activating factor directly inhibits proliferation, migration, and uPAR expression of prostate cancer cells. PLoS One. 2010 Oct 18;5(10):e13428.
Journal articles
Effect of the Gc-derived Macrophage-activating Factor Precursor (preGcMAF) on Phagocytic Activation of Mouse Peritoneal Macrophages β-Galactosidase Treatment Is a Common First-stage Modification of the Three Major Subtypes of Gc Protein to GcMAF Antitumor Effect of Degalactosylated Gc-Globulin on Orthotopic Grafted Lung Cancer in Mice
Patents
Patent No. 5701587 (Proteins that specifically bind to vitamin D-binding proteins) Patent No. 5860401 (Method for producing a novel galactose deglycosylated form of Gc globulins)

